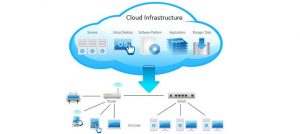
computing is the metaphor to the internet and it is a recent technology whose aim is to deliver IT services on demand on pay per usage basis to the masses. The essential key characteristics of cloud computing providers are scalability, availability, reliability, flexibility, security and serviceability etc. Clouds can be classified into three types, Public, Private and Hybrid clouds as per the deployment model. According to services provided by the cloud computing it is categorized into Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS) and Software as a Service (SaaS).
IaaS supports operations, including storage, hardware, servers and networking components. The service provider owns the equipment and is responsible for housing, running and maintaining it E.g. AWS, IBM etc. PaaS is the second model in cloud computing which acts as an intermediate between IaaS and SaaS by giving support to the IaaS to avail the services of SaaS to the end users. Platform as a Service (PaaS) is an application development and deployment platform delivered as a service to the developers over the web, e.g. Google Apps Engine, Windows Azure. Third model is SaaS where users simply make use of a web-browser to access software that others have developed and offer as a service over the web. At the SaaS level, users do not have control or access to the underlying infrastructure being owned by the host. SaaS is service model where application services are delivered over the network on a subscription and on-demand basis e.g. Google Docs, Salesforce.com etc.
Benefits of cloud computing is reduction of capital investment, automated update of the services, pay per use, more storage and mobility. The main demerits are dependent on internet connections, abiding of service provider rules and regulation at any cost and security implications. Keywords: Cloud computing, IaaS, PaaS, SaaS, Google Apps Engine, Windows Azure.